Cervical spondylosis is a common age-related disorder that affects the cervical spine, which is the portion of the spine that supports the neck. The causes of cervical spondylosis include wear and tear of the spinal disks and the bones of the neck, which can lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in the neck.
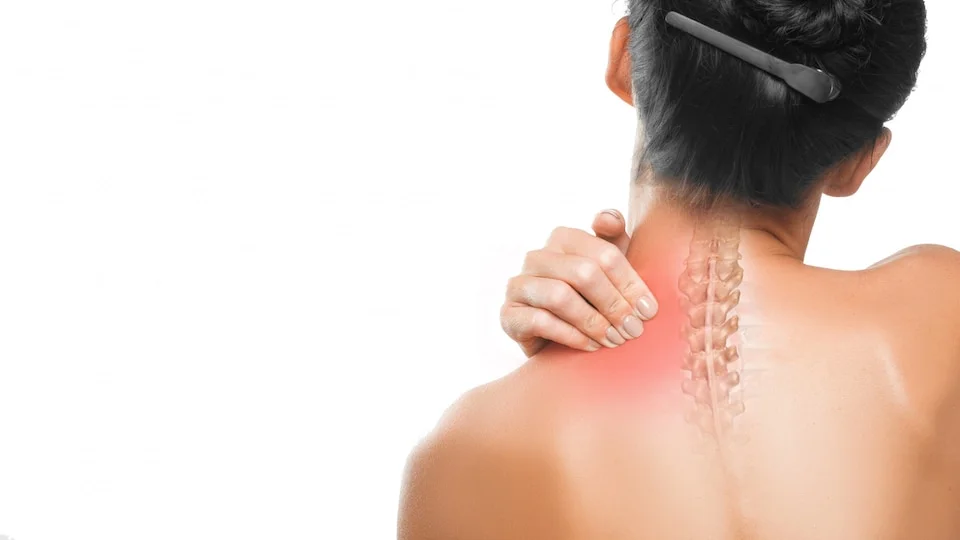
Causes of Cervical Spondylosis
There are several reasons that can contribute to the development of cervical spondylosis. The below mentioned are some of the common causes:
Age
Age is one of the main causes of cervical spondylosis. As we age, the spinal disks lose their ability to absorb shock, and the bones in the neck begin to deteriorate. This can cause the spinal discs to bulge or herniation, leading to cervical spondylosis. This wear and tear can also lead to the formation of bone spurs, which can further narrow the space available for the spinal cord and nerves.
In addition, the ligaments in the neck can become stiffer and less flexible as we age, making it harder for the neck to move and increasing the risk of injury or strain. The combination of these factors can cause neck pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility, as well as headaches, shoulder pain, and tingling or numbness in the arms or hands.
Genetics
Some people may be more prone to developing cervical spondylosis due to genetic factors. This is because the shape and size of the neck bones and spinal disks are inherited, and some people may be born with a higher risk of developing this condition.
Poor Posture
Poor posture is a common contributing factor to the development of cervical spondylosis. Maintaining good posture helps to keep the spine in its natural alignment and reduces the amount of stress placed on the neck and back muscles. Poor posture, conversely, can cause the spine to become misaligned, which can lead to wear and tear on the spinal disks and bones of the neck.
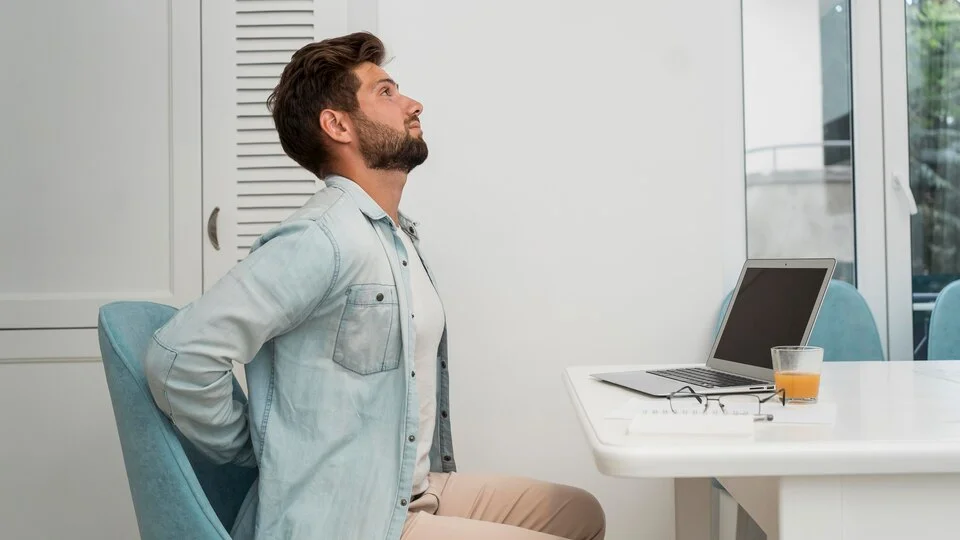

People who spend a lot of time seated at a desk or using electronic devices are particularly prone to developing poor posture, as they may hunch forward and crane their necks to see their screens. This can cause the neck to become bent in an unnatural position, putting strain on the muscles and ligaments and increasing the risk of developing cervical spondylosis.
Repetitive motions
Repetitive motions can also be a contributing factor in the development of cervical spondylosis. Motions performed repeatedly that involve the neck, such as frequently looking up or down, twisting the neck, or carrying heavy loads on the shoulders, can place additional stress on the spinal disks and bones of the neck. Over time, this wear and tear can cause development of cervical spondylosis.
Jobs or activities that require repetitive neck movements, such as assembly line work or sports that involve frequent head movements, can increase the risk of developing cervical spondylosis. Additionally, poor ergonomics or using equipment that is not properly adjusted to the individual’s height and reach can also contribute to the development of cervical spondylosis.
To reduce the risk of developing cervical spondylosis due to repetitive motions, it is important to take regular breaks and stretch the neck and shoulders throughout the day. Using proper ergonomic techniques and equipment can also help to reduce the risk of developing cervical spondylosis.
Injuries
It can also be a contributing factor in the development of cervical spondylosis. Injuries to the neck, such as whiplash from a car accident or a sports-related injury, can cause damage to the spinal disks, ligaments, and bones in the neck. This damage can lead to instability in the neck and increased wear and tear on the spinal disks, increasing the risk of developing cervical spondylosis.
In addition to acute injuries, chronic injuries from activities such as heavy lifting or repeated impacts can also increase the risk of developing cervical spondylosis over time.

Lifestyle factors
Lifestyle factors can also play a role in the development of cervical spondylosis. For example:
- Lack of physical activity: An immobile lifestyle can contribute to the development of cervical spondylosis. Exercise helps to strengthen the muscles that support the neck and improve overall spinal health.
- Smoking: Smoking can lead to the development of cervical spondylosis by reducing blood flow to the spinal disks, which can accelerate their degeneration.
- Poor diet: A diet that is high in processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats may contribute to the development of cervical spondylosis by promoting inflammation and oxidative stress in the body.
- Obesity: Excess weight can put extra strain on the spinal disks and bones in the neck, increasing the risk of developing cervical spondylosis.
- Stress: Chronic stress can lead to muscle tension in the neck & shoulders, which can increase the risk of developing cervical spondylosis over time.
Making lifestyle changes, such as including regular exercise into your routine, quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet and managing stress, can help to reduce the chance of developing cervical spondylosis.
Cervical spondylosis is a common condition that affects the spine in the neck and can cause a range of symptoms. A combination of factors including age, genetics, poor posture, repetitive motions, injuries, and lifestyle factors can cause it as well. While some of these factors, such as age and genetics, cannot be prevented, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the chance of developing cervical spondylosis or slow its progression. These include practicing good posture, incorporating regular exercise into your routine, managing stress, avoiding repetitive motions, maintaining a healthy weight, and seeking prompt medical attention for injuries or symptoms.
Raha Ayurveda- Providing the Best Ayurvedic Treatment For Cervical Spondylosis
The Ayurvedic treatment for cervical spondylosis offered by Raha Ayurveda aims to not only alleviate neck pain but also aid in regaining muscular strength, repairing damaged structures, and nourishing bones and associated tissues. By addressing nerve compressions, Cervical spondylosis ayurvedic treatments contribute to relieving patients from radiating pain that may extend towards the head, shoulder, or hands.
Leave a Reply